How to Get Rid of Alcohol in Your System
Alcoholic beverages such as beer, wine and liquor break down differently in each person's body. The substance is absorbed into the bloodstream through the stomach and the walls of the small intestines, affecting the kidneys, bladder, liver, lungs and skin.
It takes time for alcohol to leave your system. On average, it takes about one hour for the body to eliminate one standard drink. Individuals who have higher tolerances to alcohol, such as people with alcohol addiction, may eliminate alcohol more quickly.
The more you drink, the longer it takes for alcohol to leave your body. One standard drink, which is equal to 12 ounces of regular beer, will generally raise a 150-pound adult's blood alcohol content to between 0.02 and 0.03. However, the affect that one drink will have on the percentage of alcohol in your blood can vary greatly according to a complex group of personal factors.
Factors that determine how long alcohol stays in your body include liver size, body mass and the amount of alcohol consumed. A small amount of alcohol is removed from the body through sweat, urine and respiration. Alcohol can be detected in sweat, urine and the breath for at least as long as the liver is breaking down alcohol.
How Long Can Tests Detect Alcohol?
Alcohol — or ethanol — tests can detect alcohol metabolites in urine, breath, saliva, sweat and blood for between two and 80 hours. Many people believe that an alcohol metabolite called ethyl glucuronide can be detected by ETG tests for about 80 hours. But a 2007 study published in the journal Alcohol and Alcoholism found that ETG tests failed to detect alcohol more than 26 hours after consumption.

Most drug tests detect alcohol for between two and 24 hours. Hair tests can detect alcohol for up to 90 days.
Urine tests can detect alcohol for between 12 hours and 24 hours. This length of time usually depends on how recently and how much you drank. Breathalyzers can detect alcohol in your breath up to 24 hours after drinking.
Saliva tests can detect alcohol two hours after consumption, and hair tests can detect alcohol for up to 90 days.
How Does the Body Remove Alcohol?
Upon consumption, alcohol enters the stomach and intestines. Once the substance enters the capillaries surrounding the stomach and small intestines, it enters passageways that lead to the portal vein, which passes through the liver and branches out into the capillaries.
When the substance enters the bloodstream, it affects all major organs in your body, including the heart and brain. That's why heavy drinking can cause a variety of alcohol-related diseases and disorders. Alcohol reaches all body tissues except bone and fat.
The liver breaks down most of the alcohol, though the substance also passes through the kidneys, urine, skin and lungs.
Heavy drinking can eliminate vitamins and minerals from the body, which can lead to a hangover. Hangovers make you feel fatigued or sick because of the reduction in vitamin B. That's why people who attend alcohol rehab often receive nutritional support during recovery.
How the Liver Processes Alcohol
Ninety percent of alcohol consumed passes through the liver. The organ breaks down the alcohol into acetaldehyde, a chemical the body recognizes as toxic. Acetaldehyde metabolizes into carbon dioxide, which the body can eliminate.
In some cases, the production of acetaldehyde is insufficient. This leads to some people experiencing flushing, a sudden reddening of the skin that often occurs in the face or neck region. Flushing can lead to dizziness, nausea or vomiting.
The liver eliminates alcohol at a fixed rate. A healthy liver will eliminate one normal-sized alcoholic beverage in about one hour. After a night of heavy drinking your BAC may still be over the legal driving limit the next morning.
Factors that Affect BAC
Genetic, environmental, and physical and mental health factors control alcohol metabolism and elevate your blood alcohol content — the percentage of alcohol in the blood.
![]()
Food
Your body absorbs alcohol more slowly when you have food in your stomach. Those who drink on an empty stomach will feel the effects of alcohol more quickly. A person who has not eaten will hit their peak blood alcohol level between 30 minutes and two hours after consumption, depending on the amount of alcohol consumed.
Eating high protein foods, such as tofu or cheese, before or while drinking can slow the absorption of alcohol.
![]()
Strength of drink
Some drinks are stronger than others. According to the Division of Student Affairs at the University of Notre Dame, a standard drink equals:
 1.25 ounce 80 proof liquor
1.25 ounce 80 proof liquor
 12 ounce Beer
12 ounce Beer
 7 ounce Malt Liquor
7 ounce Malt Liquor
 4 to 5 ounce Wine
4 to 5 ounce Wine
Drinking stronger alcoholic beverages can accelerate the absorption rate. This causes alcohol to stay in your system for longer periods of time.
![]()
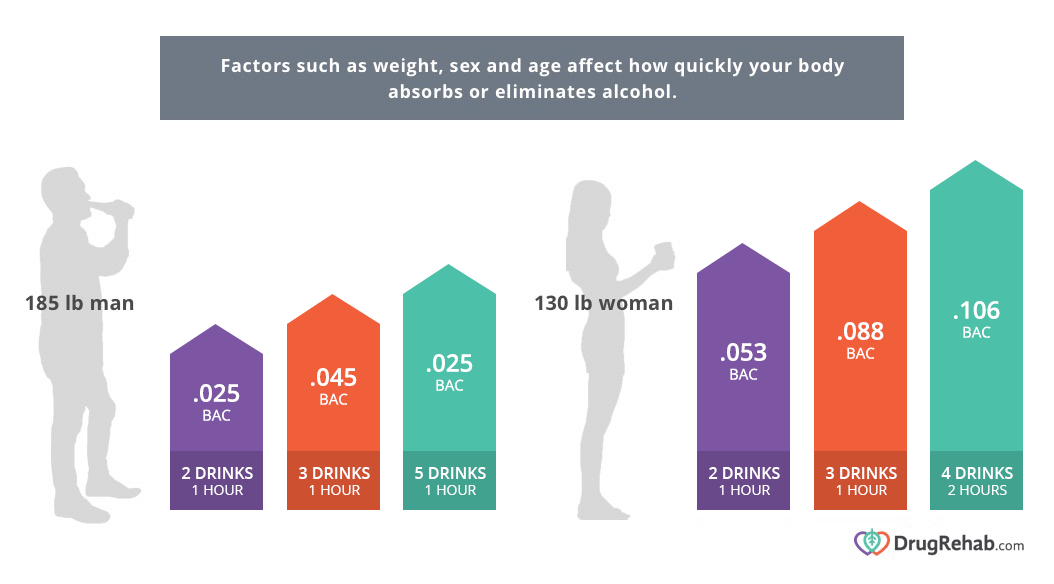
Biological Sex and Body Weight
Men and women break down alcohol at different rates. Women have less dehydrogenase, an enzyme that breaks down alcohol in the stomach. This contributes to women reaching higher blood alcohol levels than men despite drinking the same amount of alcohol.
For example, a 140-pound man who drinks two alcoholic beverages in one hour will have a blood alcohol content of 0.038. A 140-pound woman who consumed just as many drinks in one hour has a BAC of 0.048.
| Number of Standard Drinks | Duration of Drinking | BAC | Time Until BAC Reaches Zero |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two | One Hour | 0.025 | About one hour |
| Three | One Hour | 0.045 | Three hours |
| Five | One Hour | 0.085 | Just over five hours |
Source: University of Notre Dame, Division of Student Affairs
Meanwhile, a 130-pound woman will reach inebriation at a much different rate.
| Number of Standard Drinks | Duration of Drinking | BAC | Time Until BAC Reaches Zero |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two | One Hour | 0.053 | Just over three hours |
| Three | One Hour | 0.088 | Nearly six hours |
| Four | Two Hours | 0.106 | About seven hours |
Source: University of Notre Dame, Division of Student Affairs
Hormone levels also affect BAC. Women who drink their normal amount of alcohol prior to menstruation will experience higher BACs than they otherwise would.
Women also tend to have a higher percentage of body fat and a lower percentage of water, which influences intoxication and the length of time it takes to get alcohol out of their system.
AM I AN ALCOHOLIC?Take our 11-question quiz to find out now.
![]()
Mood
Your mood can affect alcohol consumption. It can also affect the way the body reacts to alcohol. Euphoric effects generally occur at a BAC of 0.02 to 0.05. Once a BAC reaches about 0.07, the drinker's mood may worsen.
If someone with alcohol problems also battles depression, their symptoms may worsen when drinking. Similarly, people with anxiety who drink heavily may experience stressful emotions that can cause a change in the stomach's enzymes, which affects how a person breaks down alcohol.
![]()
Age
Age plays an integral factor in reaching intoxication. For example, senior citizens are particularly vulnerable to alcohol because of age-related changes to their bodies. Older people experience a decrease in body water, loss of muscle tissue and decreased metabolism — all of which affects alcohol absorption.

How Long Does it Take to Sober Up?
The body generally eliminates 0.015 grams of alcohol per deciliter of blood each hour. While just about everyone breaks down alcohol at this rate, a report from the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism states that women appear to eliminate alcohol from the bloodstream faster than men.
If someone's blood alcohol content is 0.08, it would take about five hours and 20 minutes for the body to metabolize the alcohol. It typically takes a person with a BAC of 0.20 anywhere from 12 to 14 hours to reach sobriety.
Some drinks take longer for the body to metabolize than others. According to the U.K. National Health Service, it takes the body about one hour to break down a shot of liquor, two hours to break down a pint of beer and three hours to process 250 milliliters of wine.
| BAC | Time |
|---|---|
| 0.04 | 2.5 hours |
| 0.08 | 5 hours |
| 0.10 | 6.25 hours |
| 0.16 | 10 hours |
| 0.20 | 12.5 hours |
Source: Southern Illinois University Student Health Services
While people or online sources may recommend a variety of methods that they say will quickly eliminate alcohol from the body and help you pass a workplace or court-ordered alcohol test, nothing you do can speed up the process.
The only way to get sober or clear alcohol from your system is to give your liver time to break down the alcohol.
Common Myths About Sobering Up
Many people believe that drinking certain liquids or engaging in physical activity can help the body metabolize alcohol more quickly. And many companies market products that claim to quickly flush alcohol from your system. However, it is a myth that these methods are effective.
- Exercising
- Eating after drinking
- Vomiting
- Drinking coffee, energy drinks or similar beverages
- Taking a cold shower
While these techniques create the illusion of sobriety, they have no effect on BAC. Although eating before a night of drinking will slow down alcohol absorption, it will not keep you sober as you continue to drink. Eating after a few drinks will not reduce your level of intoxication because food does not have an effect on alcohol that has already been absorbed into the bloodstream.
Medical Disclaimer: DrugRehab.com aims to improve the quality of life for people struggling with a substance use or mental health disorder with fact-based content about the nature of behavioral health conditions, treatment options and their related outcomes. We publish material that is researched, cited, edited and reviewed by licensed medical professionals. The information we provide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. It should not be used in place of the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider.
How to Get Rid of Alcohol in Your System
Source: https://www.drugrehab.com/addiction/alcohol/how-long-does-alcohol-stay-in-your-system/